
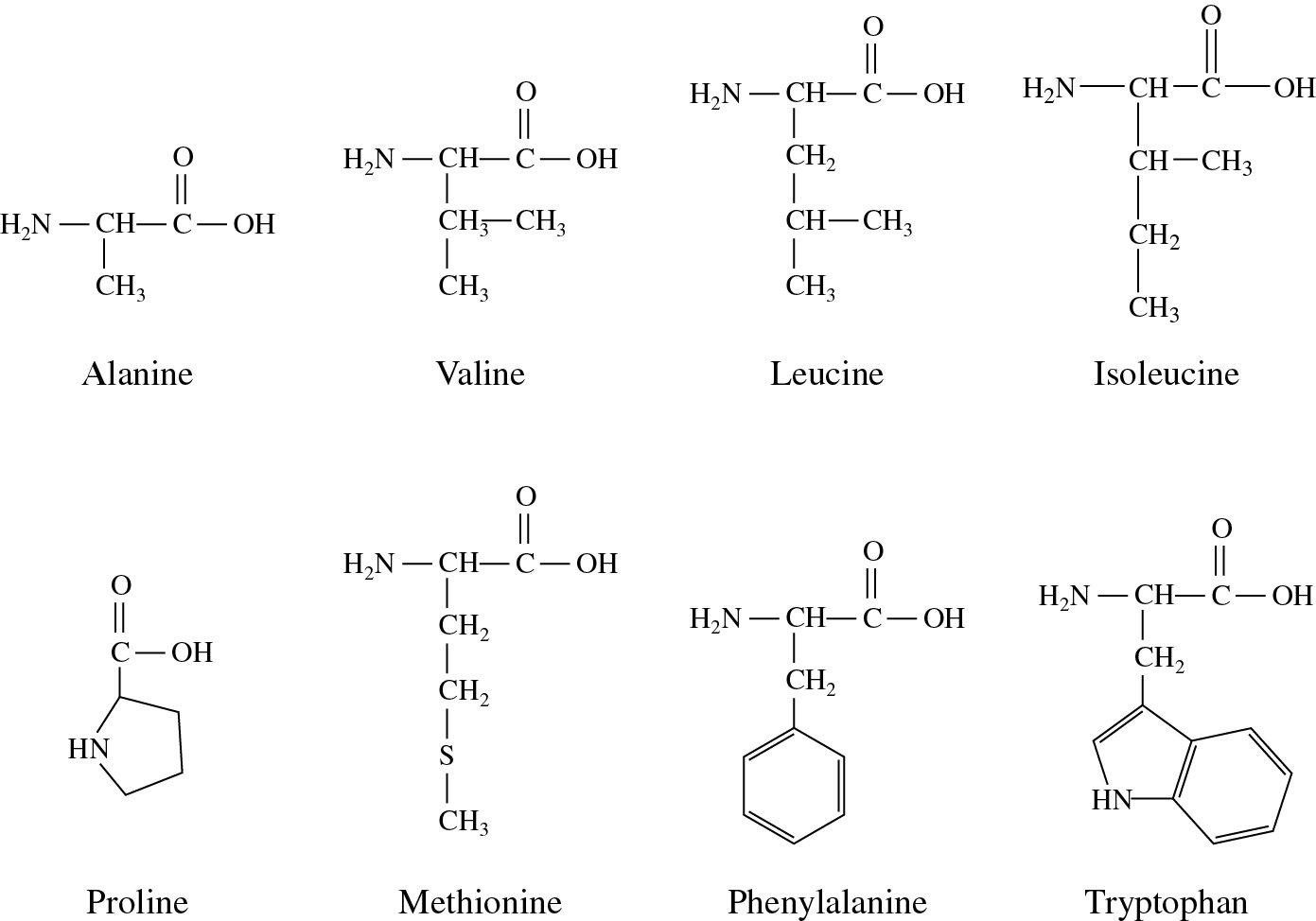
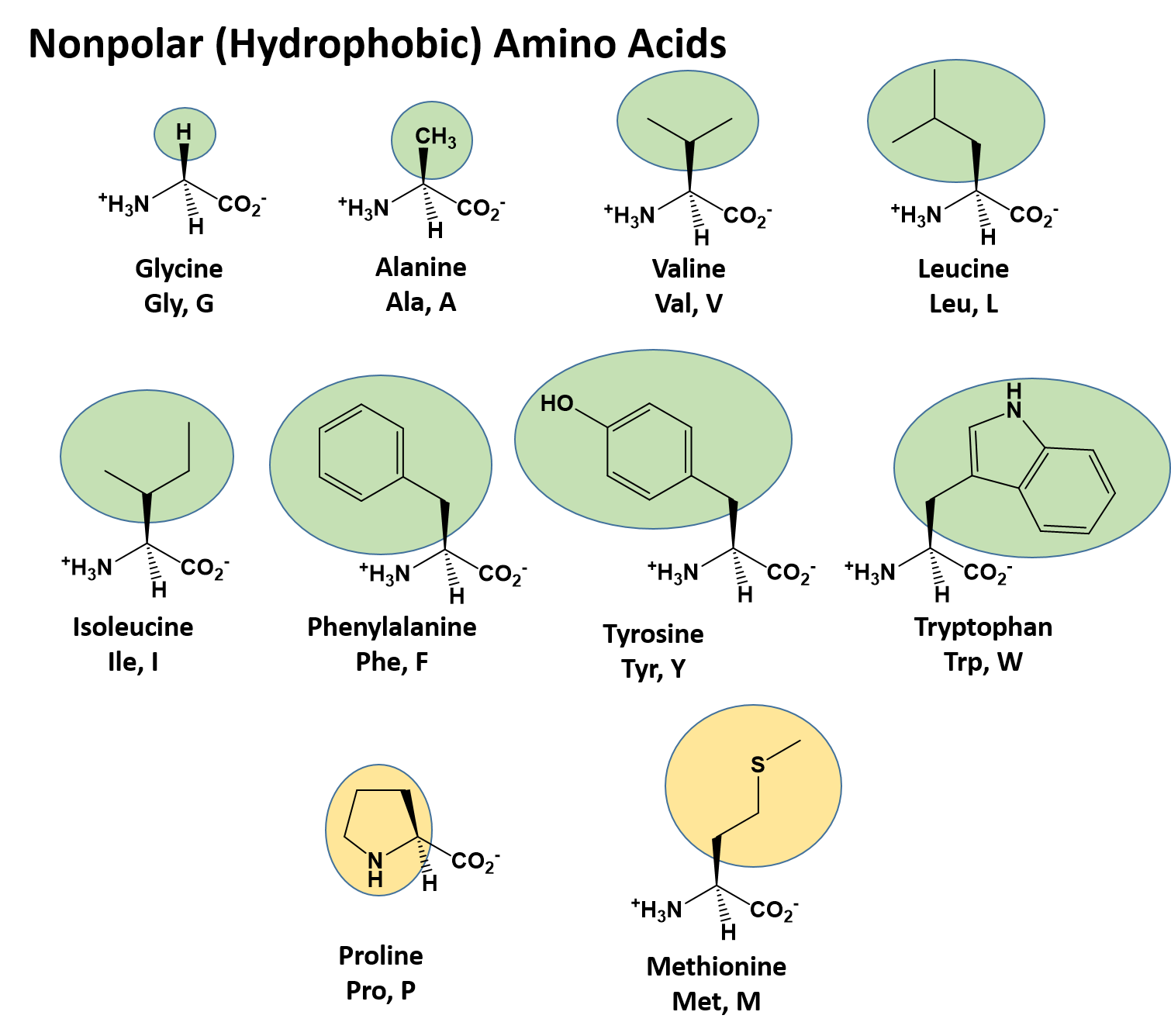

Instead, it's about the types of bonds between atoms. There are only five atoms that will appear in your amino acid variable groups: H, C, N, O, and S.Īlso, how do you know if a functional group is polar or nonpolar? Polarity isn't determined by the 'type of molecule' meaning functional group or not. The lack of polarity means they have no way to interact with highly polar water molecules, making them water fearing. Hydrophobic amino acids have little or no polarity in their side chains. Subsequently, one may also ask, how do you know if an amino acid is hydrophobic or hydrophilic? If no partial charges, it's a nonpolar amino acid. Our results offer a road map to mechanistically understand how fluorination alters hydrophobicity of (bio)polymers.While this won't tell you if a given atom achieves a full charge, or only a partial charge it's sufficient to let you know if there are atoms in a side chain with partial charges… Which means that side chain has polar elements. Changes in ΔGHyd reflect two main contributions: (i) fluorination alters side chain-water interactions we identify a crossover point from hydrophilic to hydrophobic fluoromethyl groups which may be used to estimate the hydrophobicity of fluorinated alkyl side-chains (ii) fluorination alters the number of backbone-water hydrogen bonds via changes in the relative side chain-backbone conformation. Fluorination changes ΔGHyd by -1.5 to +2 kcal mol-1, but the number of fluorines is a poor predictor of hydrophobicity. We use molecular dynamics simulations, together with a new fixed-charge, atomistic force field, to quantify the changes in hydration free energy, ΔGHyd, for amino acids with alkyl side chains and with 1 to 6 -CH → -CF side chain substitutions. Key to the impact of fluorination on protein properties is the hydrophobicity of fluorinated amino acids. Fluorination can dramatically improve the thermal and proteolytic stability of proteins and their enzymatic activity.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
